The Economic Ripple Effects of MICE
The Economic Impact on the Region
MICE is said to have a broad economic and consumption impact, encompassing activities such as conference organization, accommodation, dining, and tourism. In addition, participants tend to stay for relatively longer periods. As a result, MICE is expected to generate greater economic benefits for surrounding areas compared to general tourism.
For example, looking at the average spending per foreign participant, international conferences—classified under the "C" (Convention) category of MICE—show an average expenditure of approximately 549,000 yen per person.
This is 2.58 times higher than the average travel spending of general inbound tourists, which stands at around 213,000 yen per person.
In this way, the consumption and related business expenditures of organizers, participants, and exhibitors involved in MICE events generate significant economic ripple effects, particularly in the regions where the events are held.
Economic Ripple Effects (2023)
| Economic ripple effects from international MICE | Approximately 892.33 trillion yen |
|---|---|
| Newly generated employment effect | Approximately equivalent to 85,313 jobs |
| Tax revenue effect | Approximately 110.17 billion yen |
| Average spending per foreign participant at International conferences | Approximately 549,000 yen |
| Average travel spending per inbound tourist | Approximately 213,000 yen(※) |
In comparison, the average spending per foreign participant at International conferences is 2.58 times higher than that of general inbound tourists.
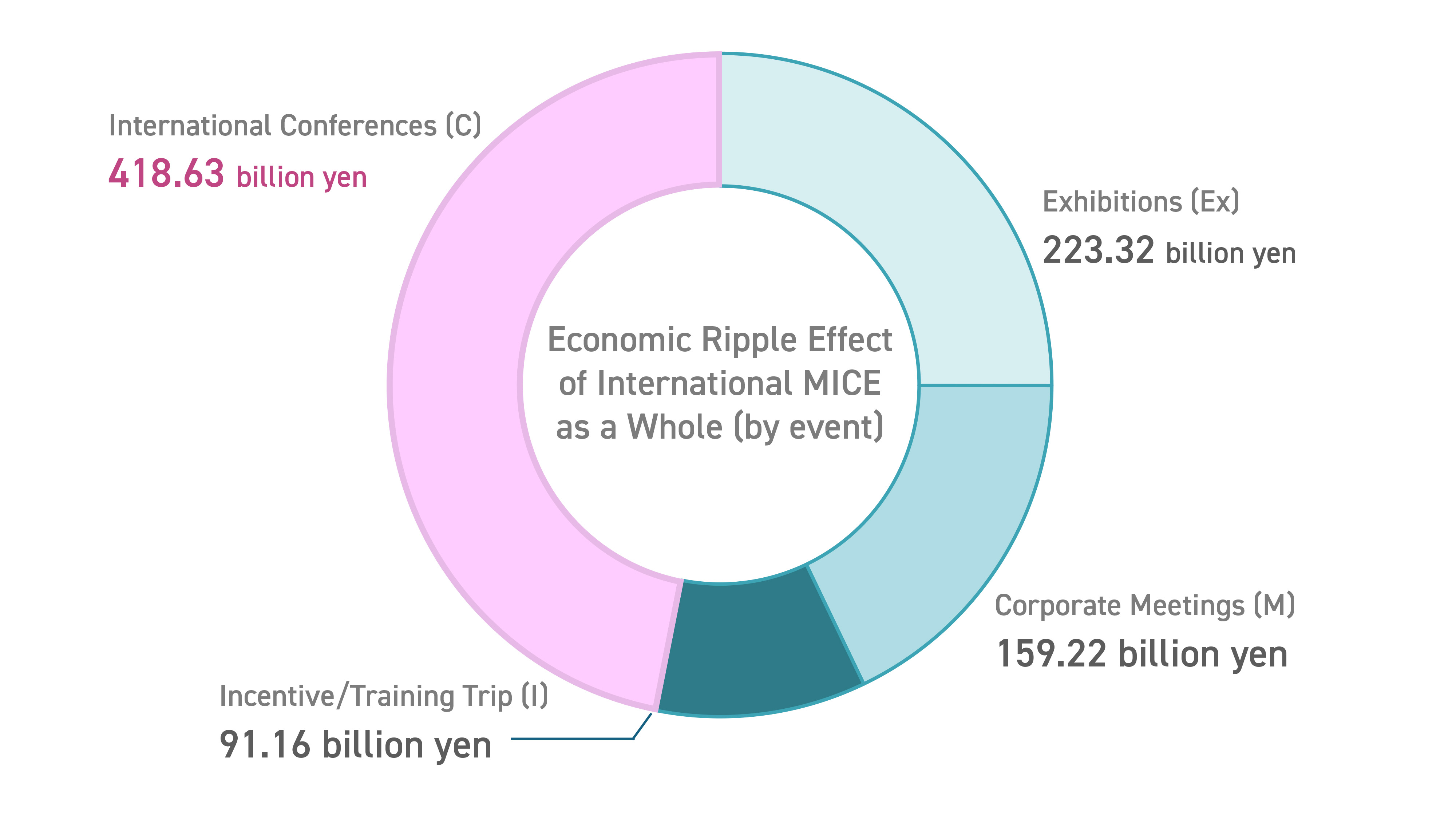
Prepared based on the Japan Tourism Agency’s “Reiwa 7 (FY2024) Report on the Economic Impact of MICE.” (updated June 30, 2025)
- Source of average travel spending per inbound tourist: Japan Tourism Agency, 2023 Consumption Trends of International Visitors to Japan (Final Report)